技术教程破解资源
2022祥云杯CTF 中babyparser 的题解
2022祥云杯CTF 中babyparser 的题解
这道题是比赛结束前3小时放出来的, 最后是0解。 我有理由怀疑这是一道防ak题。
原题附件需要glibc2.34,但我的kali版本不够高,所以我patchelf成自编译的2.34,也因此搞丢了原题附件,现在上传的是patchelf以后的版本, 如果有需要可以自己patch回去。
比赛时的逆向
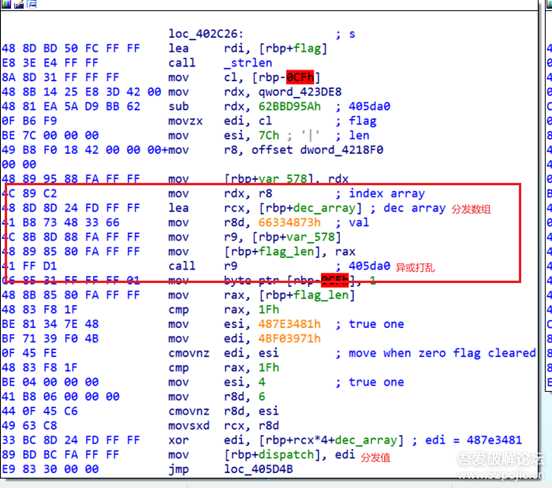
比赛时候打开一看啊,发现这个程序用了ollvm的deflat来进行混淆,而且仔细一看是个全混淆,所有能混淆的地方它都混淆了。还好之前有所准备,拿起了之前备好的脚本准备一把梭。 梭完一看发现失败了,原来是这个ollvm改良过,出题人修改了deflat的llvm pass ,分发逻辑增加了一步。 其中真实块的样子大概是这样的
这时候我以为出题人把打乱的函数都用上图中类似的call rax 间接调用来实现。 此时我心态平和,我以为还剩三小时放出来的题必不会很难,于是想尝试修改上面那个基于angr的deflat脚本。我低估了其中的难度,对于angr本身也不熟悉的我根本改不来。所以最后尝试动调加手动patch binary。 但是只是尝试了一会我就发现这个做不到,因为量太大了。因此最后决定这题先放弃,跑去做别的了。
赛后复盘
去混淆
赛后当然还是想把这道题deflat出来, 于是在之前的基础上学习了angr的用法,折腾了几天,发现angr作为符号执行的工具对于这种去混淆的处理其实并不是很合适。 因为deflat部分的处理本质上是在模拟执行程序,并且记录真实的控制流,而这部分并不是angr所擅长的。那么谁更合适呢? 当然是模拟执行的神器unicorn!
转头去尝试用unicorn完成deflat后,这题终于也走上了正轨。找了已有的unicorn deflat脚本,并在此基础上进行更改,写出了一个deflat脚本:
#coding=utf-8import collectionsimport angrimport am_graphfrom util import * # from keystone import *from unicorn import *from unicorn.x86_const import *from capstone import *from capstone.x86 import *obfus = [0x405DA0, 0x417610, 0x4149D0]def reg_ctou(regname:str): # This function covert capstone reg name to unicorn reg const. # https://github.com/unicorn-engine/unicorn/blob/master/bindings/python/unicorn/x86_const.py mp = { 'INVALID' : 0, 'AH' : 1, 'AL' : 2, 'AX' : 3, 'BH' : 4, 'BL' : 5, 'BP' : 6, 'BPL' : 7, 'BX' : 8, 'CH' : 9, 'CL' : 10, 'CS' : 11, 'CX' : 12, 'DH' : 13, 'DI' : 14, 'DIL' : 15, 'DL' : 16, 'DS' : 17, 'DX' : 18, 'EAX' : 19, 'EBP' : 20, 'EBX' : 21, 'ECX' : 22, 'EDI' : 23, 'EDX' : 24, 'EFLAGS' : 25, 'EIP' : 26, 'ES' : 28, 'ESI' : 29, 'ESP' : 30, 'FPSW' : 31, 'FS' : 32, 'GS' : 33, 'IP' : 34, 'RAX' : 35, 'RBP' : 36, 'RBX' : 37, 'RCX' : 38, 'RDI' : 39, 'RDX' : 40, 'RIP' : 41, 'RSI' : 43, 'RSP' : 44, 'SI' : 45, 'SIL' : 46, 'SP' : 47, 'SPL' : 48, 'SS' : 49, 'CR0' : 50, 'CR1' : 51, 'CR2' : 52, 'CR3' : 53, 'CR4' : 54, 'CR8' : 58, 'DR0' : 66, 'DR1' : 67, 'DR2' : 68, 'DR3' : 69, 'DR4' : 70, 'DR5' : 71, 'DR6' : 72, 'DR7' : 73, 'FP0' : 82, 'FP1' : 83, 'FP2' : 84, 'FP3' : 85, 'FP4' : 86, 'FP5' : 87, 'FP6' : 88, 'FP7' : 89, 'K0' : 90, 'K1' : 91, 'K2' : 92, 'K3' : 93, 'K4' : 94, 'K5' : 95, 'K6' : 96, 'K7' : 97, 'MM0' : 98, 'MM1' : 99, 'MM2' : 100, 'MM3' : 101, 'MM4' : 102, 'MM5' : 103, 'MM6' : 104, 'MM7' : 105, 'R8' : 106, 'R9' : 107, 'R10' : 108, 'R11' : 109, 'R12' : 110, 'R13' : 111, 'R14' : 112, 'R15' : 113, 'ST0' : 114, 'ST1' : 115, 'ST2' : 116, 'ST3' : 117, 'ST4' : 118, 'ST5' : 119, 'ST6' : 120, 'ST7' : 121, 'XMM0' : 122, 'XMM1' : 123, 'XMM2' : 124, 'XMM3' : 125, 'XMM4' : 126, 'XMM5' : 127, 'XMM6' : 128, 'XMM7' : 129, 'XMM8' : 130, 'XMM9' : 131, 'XMM10' : 132, 'XMM11' : 133, 'XMM12' : 134, 'XMM13' : 135, 'XMM14' : 136, 'XMM15' : 137, 'XMM16' : 138, 'XMM17' : 139, 'XMM18' : 140, 'XMM19' : 141, 'XMM20' : 142, 'XMM21' : 143, 'XMM22' : 144, 'XMM23' : 145, 'XMM24' : 146, 'XMM25' : 147, 'XMM26' : 148, 'XMM27' : 149, 'XMM28' : 150, 'XMM29' : 151, 'XMM30' : 152, 'XMM31' : 153, 'YMM0' : 154, 'YMM1' : 155, 'YMM2' : 156, 'YMM3' : 157, 'YMM4' : 158, 'YMM5' : 159, 'YMM6' : 160, 'YMM7' : 161, 'YMM8' : 162, 'YMM9' : 163, 'YMM10' : 164, 'YMM11' : 165, 'YMM12' : 166, 'YMM13' : 167, 'YMM14' : 168, 'YMM15' : 169, 'YMM16' : 170, 'YMM17' : 171, 'YMM18' : 172, 'YMM19' : 173, 'YMM20' : 174, 'YMM21' : 175, 'YMM22' : 176, 'YMM23' : 177, 'YMM24' : 178, 'YMM25' : 179, 'YMM26' : 180, 'YMM27' : 181, 'YMM28' : 182, 'YMM29' : 183, 'YMM30' : 184, 'YMM31' : 185, 'ZMM0' : 186, 'ZMM1' : 187, 'ZMM2' : 188, 'ZMM3' : 189, 'ZMM4' : 190, 'ZMM5' : 191, 'ZMM6' : 192, 'ZMM7' : 193, 'ZMM8' : 194, 'ZMM9' : 195, 'ZMM10' : 196, 'ZMM11' : 197, 'ZMM12' : 198, 'ZMM13' : 199, 'ZMM14' : 200, 'ZMM15' : 201, 'ZMM16' : 202, 'ZMM17' : 203, 'ZMM18' : 204, 'ZMM19' : 205, 'ZMM20' : 206, 'ZMM21' : 207, 'ZMM22' : 208, 'ZMM23' : 209, 'ZMM24' : 210, 'ZMM25' : 211, 'ZMM26' : 212, 'ZMM27' : 213, 'ZMM28' : 214, 'ZMM29' : 215, 'ZMM30' : 216, 'ZMM31' : 217, 'R8B' : 218, 'R9B' : 219, 'R10B' : 220, 'R11B' : 221, 'R12B' : 222, 'R13B' : 223, 'R14B' : 224, 'R15B' : 225, 'R8D' : 226, 'R9D' : 227, 'R10D' : 228, 'R11D' : 229, 'R12D' : 230, 'R13D' : 231, 'R14D' : 232, 'R15D' : 233, 'R8W' : 234, 'R9W' : 235, 'R10W' : 236, 'R11W' : 237, 'R12W' : 238, 'R13W' : 239, 'R14W' : 240, 'R15W' : 241, 'IDTR' : 242, 'GDTR' : 243, 'LDTR' : 244, 'TR' : 245, 'FPCW' : 246, 'FPTAG' : 247, 'MSR' : 248, 'MXCSR' : 249, 'FS_BASE' : 250, 'GS_BASE' : 251, 'FLAGS' : 252, 'RFLAGS' : 253, 'FIP' : 254, 'FCS' : 255, 'FDP' : 256, 'FDS' : 257, 'FOP' : 258, 'ENDING' : 259, } regname = regname.upper() return mp[regname]def get_context(): # record all X86/64 regs global mu return mu.context_save()def set_context(context:bytes): global mu if context == None : return else: mu.context_restore(context) return # callback for memory exceptiondef hook_mem_access(uc,type,address,size,value,userdata): pc = uc.reg_read(UC_X86_REG_RIP) print ('pc:%x type:%d addr:%x size:%x' % (pc,type,address,size))def hook_code(uc, address, size, user_data): global base global is_success global list_trace global relevants global next_real_block_addr global block_start_addr global branch_control global instrs_size global memset_count global nop_instruc instrs_size = size if is_success: uc.emu_stop() return # if address > end: # uc.emu_stop() # return for ins in md.disasm(bin[address-base:address -base + size], address-base): #print("> Tracing instruction at 0x%x, instruction size = 0x%x" % (address, size)) #print("> 0x%x:\t%s\t%s" % (ins.address, ins.mnemonic, ins.op_str)) # bfs 的visit array 防止陷入循环 if address in relevants: if address in list_trace: print("sssssss") uc.emu_stop() else: list_trace[address] = 1 # 找到了下一个块 if address in relevants and address != block_start_addr: is_success = True next_real_block_addr = address #print 'find:%x' % address uc.emu_stop() return #是否跳过指令 flag_pass = False if ins.mnemonic.startswith("call") : if(ins.op_str == '0x2090' and memset_count < 2): # hook memset twice memset_count += 1 ptr = uc.reg_read(UC_X86_REG_RDI) val = uc.reg_read(UC_X86_REG_ESI).to_bytes(1,'little') siz = uc.reg_read(UC_X86_REG_EDX) uc.mem_write(ptr,val*siz) flag_pass = True elif(ins.op_str not in ('rax','rbx','rcx','rdx','rsi','rdi','r8','r9','r10','r11','r12','r13','r14','r15') ): flag_pass = True elif(ins.op_str in ('rax','rbx','rcx','rdx','rsi','rdi','r8','r9','r10','r11','r12','r13','r14','r15')): func = uc.reg_read(reg_ctou(ins.op_str)) if func in obfus: nop_instruc.add((address,size)) else: flag_pass = True # 用于跳过指令 if flag_pass: uc.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RIP, address + size) return # 结束块单独处理 if ins.id == X86_INS_RET : if relevants[block_start_addr] in retn_nodes: # uc.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RIP, 0) # 必须注释掉 https://github.com/unicorn-engine/unicorn/issues/1133 is_success = False print ("ret ins in {}".format(hex(address))) uc.emu_stop() return else: # in obfus function pass #ollvm branch if ins.mnemonic.startswith('cmov'): #print("csel 0x%x:\t%s\t%s" %(ins.address, ins.mnemonic, ins.op_str)) regs = [reg_ctou(x) for x in ins.op_str.split(', ')] assert len(regs) == 2 v1 = uc.reg_read(regs[0]) v2 = uc.reg_read(regs[1]) if branch_control == 1: uc.reg_write(regs[0], v1) else: uc.reg_write(regs[0], v2) uc.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RIP, address + size)def find_path(start_addr,branch = None, from_error = False): global bin global base global mu global list_trace global block_start_addr global next_real_block_addr global is_success global branch_control try: list_trace = {} if from_error == False: block_start_addr = start_addr is_success = False next_real_block_addr = 0 branch_control = branch mu.emu_start(start_addr, start_addr+0x10000) # unitl 参数不重要 因为hookcode会断住 except UcError as e: pc = mu.reg_read(UC_X86_REG_RIP) if pc != 0: # 模拟执行碰到和恢复控制流无关的问题,就略过该指令继续运行 # 是一个递归,block不大的情况下应该不会递归爆炸 print(" pc:%x block_start_addr:%x" % (pc,block_start_addr)) return find_path(pc + instrs_size, branch, from_error=True) else: print("ERROR: %s pc:%x block_start_addr:%x" % (e,pc,block_start_addr)) if is_success: return next_real_block_addr return Nonedef fix(bin:bytearray,flow:dict,nop_nodes:list, patch_instrs :dict): ori_len = len(bin) # patch irrelevant blocks for nop_node in nop_nodes: fill_nop(bin, nop_node.addr-base, nop_node.size, project.arch) for a in nop_instruc: fill_nop(bin, a[0]-base, a[1], project.arch) # remove unnecessary control flows for parent, childs in flow.items(): parent = relevants[parent] if len(childs) == 1: parent_block = project.factory.block(parent.addr, size=parent.size) last_instr = parent_block.capstone.insns[-1] file_offset = last_instr.address - base # patch the last instruction to jmp if(parent.addr + parent.size == childs[0] and last_instr.op_str != hex(the_last_jmp_block)): # 下一个块就是要去的块就不用patch continue if project.arch.name in ARCH_X86: fill_nop(bin, file_offset, last_instr.size, project.arch) patch_value = ins_j_jmp_hex_x86(last_instr.address, childs[0], 'jmp') patch_instruction(bin, file_offset, patch_value) else: instr = patch_instrs[parent] file_offset = instr.address - base # patch instructions starting from `cmovx` to the end of block fill_nop(bin, file_offset, parent.addr + parent.size - base - file_offset, project.arch) if project.arch.name in ARCH_X86: # patch the cmovx instruction to jx instruction patch_value = ins_j_jmp_hex_x86(instr.address, childs[0], instr.mnemonic[len('cmov'):]) patch_instruction(bin, file_offset, patch_value) file_offset += 6 # patch the next instruction to jmp instrcution patch_value = ins_j_jmp_hex_x86(instr.address+6, childs[1], 'jmp') patch_instruction(bin, file_offset, patch_value) assert(ori_len == len(bin)) return binif __name__ == "__main__": md = Cs(CS_ARCH_X86,CS_MODE_64) md.detail = True filename = "babyparser_recover_main" new_filename = filename with open(filename, 'rb') as fp: bin = fp.read() project = angr.Project(filename, load_options={'auto_load_libs': False}) base = project.loader.main_object.mapped_base 12 << 12 start = 0x40fe20 the_last_jmp_block = 0x411448 #cfg = project.analyses.CFGFast(normalize=True) cfg = project.analyses.CFGFast(normalize=True,force_complete_scan=False) target_function = cfg.functions.get(start) assert target_function != None # end = start + target_function.size supergraph = am_graph.to_supergraph(target_function.transition_graph) # *******************GET BLOCK*************************** # get prologue_node(开始结点) and retn_node prologue_nodes = [] retn_nodes = [] relevant_nodes = [] nop_nodes = [] patch_instrs = {} for node in supergraph.nodes(): if supergraph.in_degree(node) == 0: prologue_nodes.append(node) elif supergraph.out_degree(node) == 0 : retn_nodes.append(node) elif supergraph.out_degree(node) == 1 and node.addr != the_last_jmp_block: relevant_nodes.append(node) elif supergraph.out_degree(node) == 2 : nop_nodes.append(node) print(prologue_nodes) print(retn_nodes) if len(prologue_nodes) != 1 or prologue_nodes[0].addr != start: print("Something must be wrong...") exit(0) main_dispatcher_node = list(supergraph.successors(prologue_nodes[0]))[0] relevant_block_addrs = [(node.addr) for node in relevant_nodes] relevants = {} for node in relevant_nodes+prologue_nodes+retn_nodes: relevants[node.addr] = node print('*******************relevant blocks************************') print('prologue: %#x' % start) print('main_dispatcher: %#x' % main_dispatcher_node.addr) print('retn: ' , [hex(node.addr) for node in retn_nodes]) print('relevant_blocks:', [hex(addr) for addr in relevant_block_addrs]) print('*******************simulated execution*********************') flow = collections.defaultdict(list) instrs_size = 0 memset_count = 0 nop_instruc = set() mu = Uc(UC_ARCH_X86, UC_MODE_64) #init stack mu.mem_map(0x80000000,0x10000 * 8) # map 4MB memory for this emulation mu.mem_map(base, 16 * 1024 * 1024) # write machine code to be emulated to memory mu.mem_write(0x401000, bin[0x2000:0x2000+0x19559]) # code segment mu.mem_write(0x420dd0,bin[0x20dd0:0x20dd0+0x6270]) # data segment mu.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RSP, 0x80000000 + 0x10000 * 6) mu.hook_add(UC_HOOK_CODE, hook_code) # 对每条指令hook mu.hook_add(UC_HOOK_MEM_UNMAPPED, hook_mem_access) #set function argv mu.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RDI, 1) # set argc list_trace = {} is_debug = False queue = [(start, None)] while len(queue) != 0: env = queue.pop() address = env[0] context = env[1] if address in flow: continue set_context(context) node = relevants[address] block = project.factory.block(address, size=node.size) # 当前处理的块 has_branches = False hook_addr = [] #检测代码块中是否有ollvm生成的分支 for ins in block.capstone.insns: if ins.insn.mnemonic.startswith('cmov'): has_branches = True if node not in patch_instrs: patch_instrs[node] = ins break #代码块中有ollvm生成的分支 if has_branches: ctx = get_context() p1 = find_path(address, 0) if p1 != None: queue.append((p1, get_context())) flow[address].append(p1) set_context(ctx) p2 = find_path(address, 1) if p1 == p2: p2 = None if p2 != None: queue.append((p2, get_context())) flow[address].append(p2) else: p = find_path(address) if p != None: queue.append((p, get_context())) flow[address].append(p) # print(flow) print('************************flow******************************') for k, v in flow.items(): print('%#x: ' % k, [hex(child) for child in v]) print('************************fix******************************') new_bin = fix(bytearray(bin), flow, nop_nodes, patch_instrs) with open(new_filename,"wb") as fp: fp.write(new_bin)对于好几个关键函数进行去混淆以后,终于可以开始着手逆向了!
cpp stl 逆向
接下来就是逆向的问题了,先简单逆一下能知道,程序要求的输入是符号和数字,其中数字必须是0x[a-f][a-f][a-f][a-f] 符号只能是?!^| ,再加上题目说这是一个parser,我们可以猜到这是一个算式的解析。 那么肯定代码里会出现stack 这个stl 的数据结构, 而我对此并不是很熟悉。 果然我在动调的时候发现了sub_4151B0是一个parser功能的函数,其中它的第一个参数是这样的结构:
很有可能这就是栈的结构,我们都知道栈的默认底层container是deque, 因此去查了一下cpp里deque的实现:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/494261593 , 通过这篇博客,我们可以写出deque的结构体。 当然还有vector也是逆向中很重要的数据结构:
struct deque_iter{ obj* cur; obj* begin; obj* end; obj* cur_node;};struct deque{ ptr M_map; size_t M_map_size; deque_iter start; deque_iter finish;};struct vector{ obj begin[vector.size]; obj* obj_end; obj* capacity_end;};在ida里加入这些结构体以后再逆向,整个逻辑就清楚了很多。 ?! 相当于是() ,只有^ 和 | 是运算符。 又根据明显的先序后序遍历能知道最后parser出来的是一个二叉树。 因此知道了输入的结构是 ?0x|0x!^?0x|0x!
加密部分的处理
我们把上面处理结果的四个未知量从左到右设为a,b,c, d, 最终的比对流程简化为:
sub_40F5B("hello123",d) ^ sub_40F5B("hello456",c) == cmp1
sub_411DE0("smithsmith666666", cmp1) ^ sub_411DE0("smithsmith777777", sub_40F5B(hello123,b) ^ sub_40F5B(hello456,a) ) == cmp2
通过对sbox的分析,以及密钥里smith的读音, 可以直接猜出sub_411DE0其实是sm4 加密,但是我没有看出sub_40F5B是什么加密。
由于a b c d 四个未知量,其中每个未知量都只有$6^4$种可能,而且由于sub_40F5B是ECB模式的块加密,每一个未知量又可以分为两个部分,可能性进一步退化到$6^2$。 因此可以采用爆破的方法。 虽然我们不知道sub_40F5B是什么加密,但是也可以用unicorn 来进行模拟执行。
最终的解密代码如下:
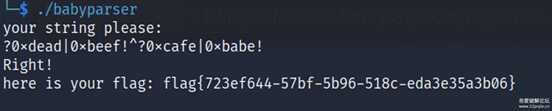
from unicorn import *from unicorn.x86_const import *from capstone import *from capstone.x86 import *from itertools import productfrom tqdm import tqdmbase = 0x3ff000def trans(a)->bytes: ret = [0]*(len(a)*4) for i in range(len(a)): ret[i*4] = ord(a[i]) return bytes(ret)candi = []for c in product('abcdef',repeat=2): candi.append(trans(c))a = list(0xB997FEA9D35F1491.to_bytes(8,'little') + 0xF199D36FCF4A12C7.to_bytes(8,'little'))# --------------------bruteforce enc--------------------# with open("./babyparser", 'rb') as fp:# bin = fp.read()# def hook_code(uc, address, size, user_data):# for ins in md.disasm(bin[address-base:address -base + size], address-base):# # print("> Tracing instruction at 0x%x, instruction size = 0x%x" % (address, size))# # print("> 0x%x:\t%s\t%s" % (ins.address, ins.mnemonic, ins.op_str))# if ins.mnemonic.startswith("call") :# if(ins.op_str == '0x2090'): # hook memset twice# ptr = uc.reg_read(UC_X86_REG_RDI)# val = uc.reg_read(UC_X86_REG_ESI).to_bytes(1,'little') # siz = uc.reg_read(UC_X86_REG_EDX)# uc.mem_write(ptr,val*siz)# uc.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RIP, address + size)# md = Cs(CS_ARCH_X86,CS_MODE_64)# md.detail = True# mu = Uc(UC_ARCH_X86, UC_MODE_64)# #init stack# mu.mem_map(0x80000000,0x10000 * 8)# # map 4MB memory for this emulation# mu.mem_map(base, 16 * 1024 * 1024)# # write machine code to be emulated to memory# mu.mem_write(0x401000, bin[0x2000:0x2000+0x19559]) # code segment# mu.mem_write(0x420dd0,bin[0x20dd0:0x20dd0+0x6270]) # data segment# mu.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RSP, 0x80000000 + 0x10000 * 6)# mu.hook_add(UC_HOOK_CODE, hook_code) # 对每条指令hook# initial = mu.context_save()# for key in [b"hello123",b"hello456"]: # b"hello123"# f = open(key.decode(), 'wb')# for can in tqdm(candi):# mu.context_restore(initial)# mu.mem_write(0x80000010,key)# mu.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RDI,0x80000010)# mu.mem_write(0x80000020,can)# mu.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RSI,0x80000020)# mu.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RDX,0x80000030)# mu.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_ECX,8)# mu.emu_start(0x40F5B0, 0x40F5F1)# enced = mu.mem_read(0x80000030,8)# f.write(can+enced)# f.close()b = list(0x26F04376032014A3.to_bytes(8,'little') + 0x4744333708D0E9AC.to_bytes(8,'little'))with open("hello123",'rb') as f: con = f.read()h123 = {}for i in range(0,len(con),0x20): h123[con[i+0x10:i+0x20]] = con[i:i+0x10]h456 = {}with open("hello456",'rb') as f: con = f.read()for i in range(0,len(con),0x10): h456[con[i+0x8:i+0x10]] = con[i:i+0x8]def brute(cmp:list): for n123 in tqdm(h123): for n456_1 in h456: for n456_2 in h456: n456 = n456_1+n456_2 tmp = [n123[i]^n456[i] for i in range(16)] if(tmp == list(cmp)): print(h123[n123],h456[n456[0:8]],h456[n456[8:16]]) #babe cafe return # ?0xdead|0xbeef!^?0xcafe|0xbabe!import sm4k1 = sm4.SM4Key(b'smithsmith666666')tmp = k1.encrypt(bytes(a)) print(tmp)cmp2 = [tmp[i]^b[i] for i in range(16)]k2 = sm4.SM4Key(b'smithsmith777777')cmp2 = k2.decrypt(bytes(cmp2))brute(cmp2) # beef dead babyparser_recover_main.txt2022-11-25 20:51 上传点击文件名下载附件
babyparser_recover_main.txt2022-11-25 20:51 上传点击文件名下载附件去混淆后
 babyparser.txt2022-11-25 20:51 上传点击文件名下载附件
babyparser.txt2022-11-25 20:51 上传点击文件名下载附件原题目文件